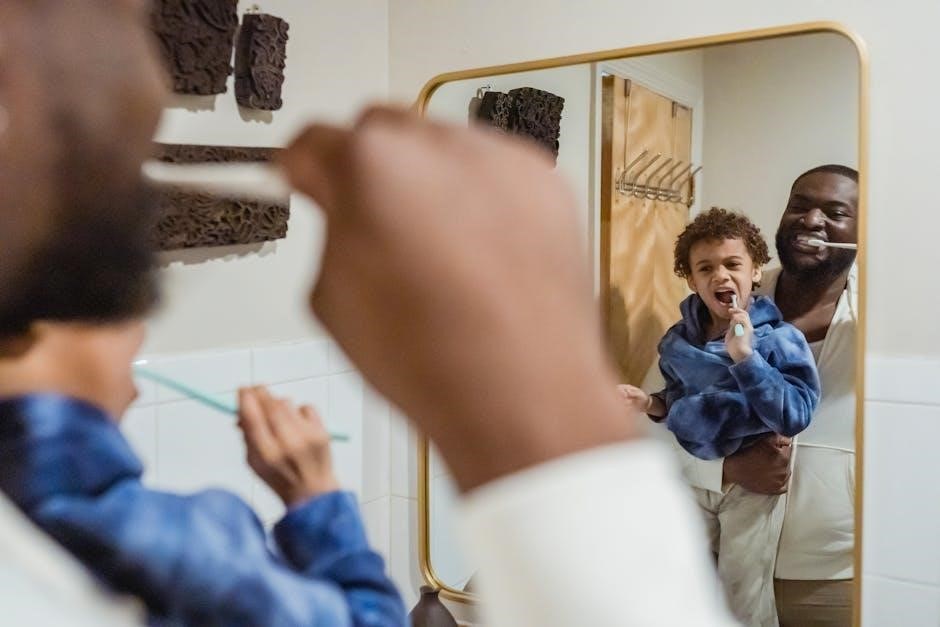
Dental Code D1330 refers to oral hygiene instructions provided by dental professionals to educate patients on proper oral care techniques‚ aiming to prevent dental issues and promote overall oral health.
1.1 Definition and Purpose of D1330
Dental Code D1330 defines oral hygiene instructions as a procedure where dental professionals educate patients on proper oral care. Its purpose is to guide patients in maintaining good oral hygiene‚ preventing dental issues‚ and promoting overall oral health through personalized advice and demonstrations.
1.2 Overview of Oral Hygiene Instructions
Oral hygiene instructions are personalized guidance provided by dental professionals to help patients maintain optimal oral health. These instructions typically include proper brushing techniques‚ flossing‚ and the use of fluoride. The goal is to empower patients with knowledge and skills to prevent dental issues‚ such as cavities and gum disease‚ and promote long-term oral well-being. Dental professionals tailor these instructions to individual needs‚ ensuring effective and sustainable oral care practices.
Importance of Oral Hygiene in Dental Care
Oral hygiene is crucial for maintaining dental health‚ preventing infections‚ and ensuring overall well-being. Proper care prevents conditions like gum disease and tooth decay‚ promoting a healthy smile.
2.1 Link Between Oral Health and Overall Well-being
Oral health significantly impacts overall well-being‚ as poor hygiene can lead to systemic conditions like heart disease‚ diabetes‚ and respiratory infections. Gum disease has been linked to increased risks of these health issues‚ emphasizing the importance of preventive care.
2.2 Consequences of Poor Oral Hygiene
Neglecting oral hygiene leads to severe consequences‚ including tooth decay‚ gum disease‚ and bad breath. If left untreated‚ these issues can progress to painful abscesses‚ tooth loss‚ and even systemic health problems like heart disease and diabetes.
Components of an Effective Oral Hygiene Routine
An effective oral hygiene routine includes brushing‚ flossing‚ fluoride use‚ and therapeutic mouthwashes. These practices work together to maintain teeth strength‚ prevent decay‚ and ensure fresh breath.
3.1 Brushing Techniques and Frequency
Proper brushing is essential for maintaining oral health. Brush teeth twice daily using a fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristled brush. Use gentle circular motions‚ ensuring all surfaces are covered. Spend two minutes brushing‚ paying special attention to areas where teeth and gums meet. Replace the toothbrush every 3-4 months or when bristles fray. Dental Code D1330 emphasizes these techniques to prevent plaque buildup and promote a healthy smile through consistent oral hygiene practices.
3.2 Role of Dental Floss and Interdental Cleaners
Dental floss and interdental cleaners are crucial for removing food particles and plaque between teeth and below the gumline‚ areas a toothbrush cannot reach. Flossing daily helps prevent gingivitis and interdental cavities. Interdental cleaners‚ such as picks or brushes‚ are ideal for tight spaces. These tools complement brushing by ensuring thorough removal of plaque‚ promoting healthier gums and preventing bad breath. Regular use enhances overall oral hygiene‚ aligning with the preventive goals of Dental Code D1330.
3.3 Use of Fluoride in Oral Hygiene
Fluoride is a natural mineral that plays a vital role in oral hygiene by strengthening tooth enamel and preventing tooth decay. It can be applied through toothpaste‚ mouthwashes‚ or professional treatments like varnishes. Fluoride helps remineralize teeth‚ making them more resistant to acid attacks from plaque and sugars. Regular fluoride use can reverse early stages of tooth decay and reduce sensitivity. It is particularly beneficial for children but also effective for adults‚ making it a cornerstone of preventive oral care under Dental Code D1330.
3.4 Therapeutic Mouthwashes: Benefits and Usage
Therapeutic mouthwashes contain active ingredients that target specific oral health concerns‚ such as gingivitis‚ plaque‚ and bad breath. Unlike cosmetic mouthwashes‚ they are designed to provide medical benefits‚ like reducing inflammation or killing bacteria. These mouthwashes may contain ingredients like chlorhexidine or essential oils. Proper usage involves following the product’s instructions‚ typically swishing the liquid around the mouth for 30 seconds before spitting it out. Regular use‚ as part of a comprehensive oral hygiene routine‚ can enhance dental health and prevent common issues‚ especially when combined with brushing and flossing.

Role of Dental Professionals in Oral Health Education
Dental professionals play a crucial role in educating patients on oral hygiene‚ providing personalized advice‚ and demonstrating techniques to improve dental health and prevent issues.
4.1 Dentist’s Responsibility in Patient Education
Dentists are key educators‚ responsible for providing personalized oral hygiene guidance. They assess patients’ needs‚ demonstrate proper brushing and flossing techniques‚ and discuss fluoride use and mouthwash benefits. By tailoring advice‚ dentists empower patients to maintain optimal oral health‚ prevent dental issues‚ and reduce future treatment costs through proactive care.
4;2 Contribution of Dental Hygienists in Oral Health Instruction
Dental hygienists play a vital role in oral health education by providing hands-on instruction and personalized care. They demonstrate proper brushing and flossing techniques‚ discuss interdental cleaning tools‚ and explain the benefits of fluoride and therapeutic mouthwashes. Hygienists often spend more time with patients‚ addressing specific concerns and tailoring advice to individual needs‚ which enhances patient understanding and adherence to oral hygiene routines‚ leading to improved dental health outcomes and increased patient confidence in maintaining their oral care effectively.
Preventive Dental Care and Its Impact
Preventive dental care‚ including oral hygiene instructions‚ significantly reduces the risk of cavities‚ gum disease‚ and other issues‚ promoting long-term oral health and lowering dental treatment costs effectively.
5.1 How Oral Hygiene Instructions Prevent Common Dental Issues
Oral hygiene instructions educate patients on proper brushing‚ flossing‚ and fluoride use‚ preventing plaque buildup and tooth decay. Regular cleaning removes bacteria‚ reducing gum disease risk. These practices also help avoid bad breath and promote healthier smiles‚ ensuring early detection of issues like cavities or gingivitis. By fostering good habits‚ oral hygiene instructions empower patients to maintain their dental health effectively‚ lowering the likelihood of costly and invasive treatments in the future.
5.2 The Role of Preventive Care in Reducing Dental Costs
Preventive dental care significantly reduces long-term costs by addressing oral health issues early. Regular cleanings and check-ups can prevent conditions like gum disease and tooth decay‚ which are costly to treat. Oral hygiene instructions empower patients to maintain good habits‚ reducing the need for extensive procedures. Early detection of problems through preventive care avoids more expensive treatments‚ making it a cost-effective approach to maintaining dental health.

Accessibility and Barriers to Dental Care
Accessibility to dental care is often hindered by economic‚ geographic‚ and systemic barriers‚ including high costs‚ lack of insurance‚ and limited availability of dental services in rural areas.
6.1 Challenges in Accessing Dental Services
Accessing dental services remains challenging for many due to economic barriers‚ such as high costs and lack of insurance‚ as well as geographic limitations in rural areas with fewer dental providers. Systemic issues‚ including limited transportation and long wait times‚ further exacerbate these difficulties‚ particularly for low-income and marginalized communities. These obstacles hinder individuals from receiving timely oral hygiene education and preventive care‚ underscoring the need for targeted solutions to improve accessibility and equity in dental care.
6.2 Strategies to Improve Access to Oral Health Education
To enhance access to oral health education‚ strategies include community outreach programs‚ partnerships with schools‚ and leveraging tele-dentistry to reach remote areas. Offering sliding-scale clinics and culturally sensitive care can address financial and social barriers. Increasing awareness through public campaigns and collaborating with local organizations can also promote dental health literacy. These efforts aim to ensure that all individuals‚ regardless of their background‚ can access essential oral hygiene instruction and preventive care.

The Future of Oral Hygiene and Dental Codes
The future of oral hygiene and dental codes like D1330 will focus on advancing technology‚ personalized care‚ and updated guidelines to improve patient outcomes and accessibility.
7.1 Emerging Trends in Oral Hygiene Practices
Emerging trends in oral hygiene practices include advancements in personalized care‚ AI-driven diagnostic tools‚ and innovative products like nano toothpaste. These trends aim to enhance efficiency and accessibility‚ making oral hygiene more tailored to individual needs. Additionally‚ there is a growing emphasis on preventive care‚ with updated guidelines and codes like D1330 playing a crucial role in standardizing education and practices. These advancements promise to revolutionize how oral health is managed and maintained in the future.
7.2 Potential Updates to Dental Codes and Guidelines
Potential updates to dental codes and guidelines‚ such as D1330‚ may include new diagnostic codes and expanded clinical practice guidelines. These updates aim to align with advancements in oral hygiene practices and technologies. Regular revisions ensure that codes reflect current research and evidence-based practices‚ improving patient outcomes. Updates may also address emerging trends‚ ensuring consistency and adaptability in dental care delivery. Staying updated helps dental professionals provide high-quality‚ standardized care‚ fostering better oral health and patient satisfaction.

Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Real-world applications of D1330 highlight successful oral hygiene programs‚ demonstrating improved patient outcomes through education and personalized care‚ reinforcing the code’s effectiveness in preventive dental strategies.
8.1 Successful Implementation of Oral Hygiene Programs
Successful oral hygiene programs often combine fluoride treatments‚ dental floss use‚ and therapeutic mouthwashes with personalized patient education. These programs emphasize regular brushing and interdental cleaning‚ reducing plaque and gingivitis. Real-world applications show improved patient compliance when instructions are tailored to individual needs‚ fostering long-term oral health. Such initiatives highlight the effectiveness of D1330 in preventing dental issues and promoting overall well-being through structured‚ evidence-based approaches.
8.2 Patient Outcomes and Feedback on Dental Code D1330
Patient outcomes from D1330 often show improved oral health‚ with reduced plaque and gingivitis due to better hygiene practices. Feedback highlights increased patient satisfaction‚ as personalized instructions enhance understanding and compliance. Many report healthier gums and fewer cavities‚ demonstrating the program’s effectiveness. Patients appreciate the tailored approach‚ emphasizing its value in preventive care. Positive responses underscore the importance of oral hygiene education in achieving long-term dental health and patient confidence.
Dental Code D1330 emphasizes the importance of oral hygiene education‚ highlighting its role in improving patient outcomes and promoting preventive dental care for long-term health benefits.
9.1 Summary of Key Points
Dental Code D1330 highlights the importance of oral hygiene education‚ emphasizing its role in preventing dental issues and promoting overall health. Proper techniques‚ such as brushing‚ flossing‚ and using fluoride‚ are essential for maintaining oral well-being. Dental professionals play a crucial role in educating patients‚ while preventive care reduces long-term dental costs. Despite barriers like accessibility‚ consistent oral hygiene practices remain vital for ensuring healthy smiles and overall well-being. This code underscores the significance of education in achieving optimal oral health outcomes.
9.2 Final Thoughts on the Importance of Oral Hygiene
Oral hygiene is foundational to overall health‚ preventing issues like decay and gum disease while boosting confidence and quality of life. Consistent practices‚ such as brushing‚ flossing‚ and using fluoride‚ are essential for long-term dental health. Dental professionals play a vital role in educating patients‚ ensuring they adopt effective routines. By prioritizing oral care‚ individuals can avoid costly treatments and maintain a healthy‚ radiant smile. The future of dental health lies in education and prevention‚ emphasizing the lasting impact of proper oral hygiene practices.

